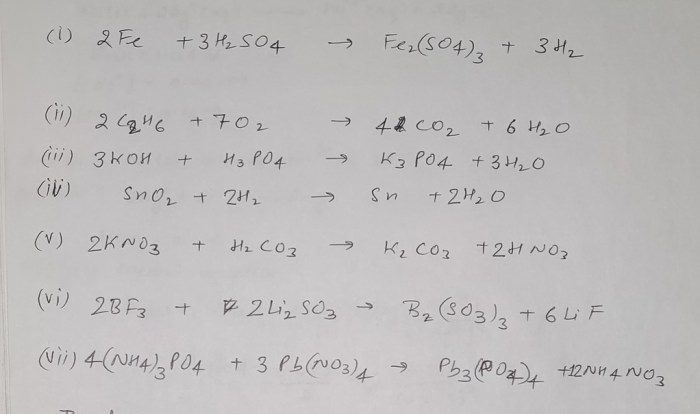Oxidation and reduction reactions worksheet – Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of oxidation and reduction reactions with our meticulously crafted worksheet. This invaluable resource delves into the fundamental concepts, types, balancing, and applications of these reactions, equipping you with a comprehensive understanding of this essential chemical process.
As we delve into the intricacies of oxidation-reduction reactions, we will unravel the mysteries of electron transfer, explore the roles of oxidizing and reducing agents, and uncover the mechanisms behind various reaction types. Through engaging examples and interactive exercises, you will gain a profound grasp of these reactions and their far-reaching impact in diverse scientific fields.
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions.
Oxidationis the loss of electrons, while reductionis the gain of electrons.
The substance that causes oxidation is called an oxidizing agent, and the substance that causes reduction is called a reducing agent.
Types of Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
- Combustion reactionsinvolve the reaction of a substance with oxygen, releasing heat and light.
- Displacement reactionsinvolve the replacement of one element in a compound by another element.
- Disproportionation reactionsinvolve the reaction of a substance to produce two or more different products, one of which is oxidized and the other is reduced.
- Combination reactionsinvolve the reaction of two or more substances to form a single product.
Balancing Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Redox reactions can be balanced using the half-reaction method, which involves separating the reaction into two half-reactions, one for oxidation and one for reduction.
The oxidation number of an element is the charge it would have if all of its bonds were ionic.
The oxidation number of an element can be used to determine whether it has been oxidized or reduced.
Applications of Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
- Batteriesstore chemical energy and convert it into electrical energy through redox reactions.
- Fuel cellsconvert the chemical energy of a fuel into electrical energy through redox reactions.
- Corrosionis the degradation of metals due to redox reactions with oxygen or other substances.
- The production of chemicalsoften involves redox reactions, such as the production of chlorine and sodium hydroxide from brine.
Example Problems
| Reactants | Products | Type of Reaction | Redox Couple |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2 | Zinc and hydrochloric acid react to form zinc chloride and hydrogen gas. | Displacement | Zn/Zn2+, H+/H2 |
| 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 | Sodium and water react to form sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. | Displacement | Na/Na+, H+/H2 |
| 2Fe + 3Cl2 → 2FeCl3 | Iron and chlorine gas react to form iron(III) chloride. | Combination | Fe/Fe3+, Cl2/Cl– |
| 2KMnO4 + 10FeSO4 + 8H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 5Fe2(SO4)3 + 8H2O | Potassium permanganate and ferrous sulfate react in acidic solution to form potassium sulfate, manganese sulfate, ferric sulfate, and water. | Redox | MnO4–/Mn2+, Fe2+/Fe3+ |
| Cu + 2AgNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2Ag | Copper and silver nitrate react to form copper(II) nitrate and silver. | Displacement | Cu/Cu2+, Ag+/Ag |
Additional Resources

- Oxidation-Reduction Reactions | Khan Academy
- Balancing Redox Reactions | Crash Course Chemistry
- Oxidation-Reduction | Britannica
Frequently Asked Questions: Oxidation And Reduction Reactions Worksheet
What is the key concept behind oxidation-reduction reactions?
Oxidation-reduction reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions, resulting in changes in their oxidation states.
How do I identify the oxidizing and reducing agents in a reaction?
The oxidizing agent is the species that accepts electrons, causing its oxidation state to decrease, while the reducing agent donates electrons, leading to an increase in its oxidation state.
Why is balancing oxidation-reduction reactions crucial?
Balancing these reactions ensures that the number of electrons lost by the reducing agent is equal to the number of electrons gained by the oxidizing agent, maintaining the overall charge balance.