The following excerpt is consonant, delving into the realm of musical harmony and the captivating role of consonance. Consonance, a cornerstone of musical aesthetics, weaves a tapestry of pleasing sounds, creating a sense of stability and resolution within musical compositions.
Throughout history, consonance has played a pivotal role in shaping musical traditions across cultures. Its harmonious nature has captivated listeners, inspiring composers to craft melodies and chords that resonate with the human ear.
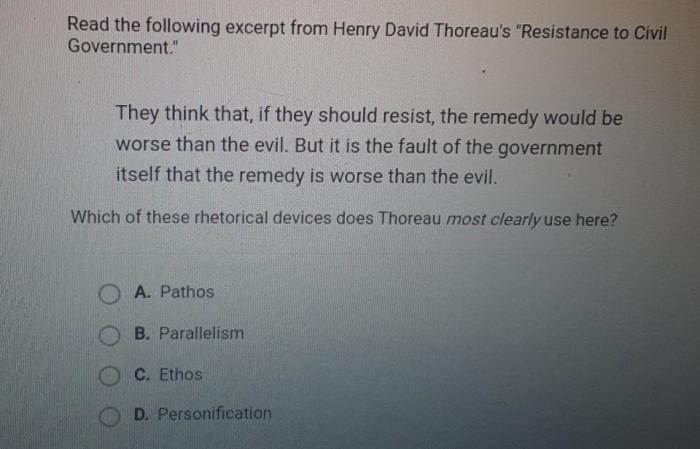
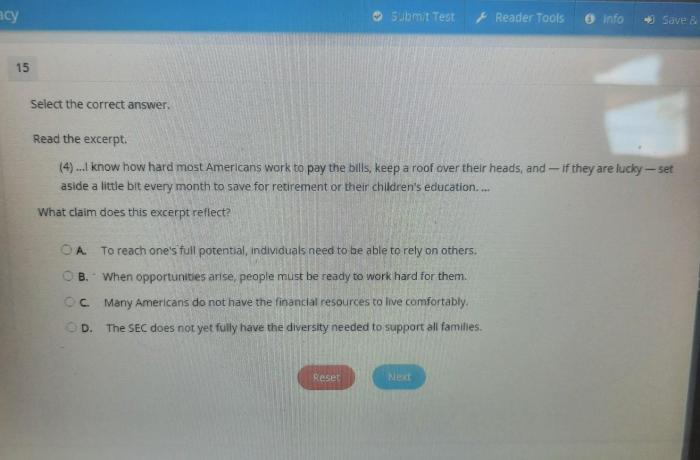
Consonance in Music
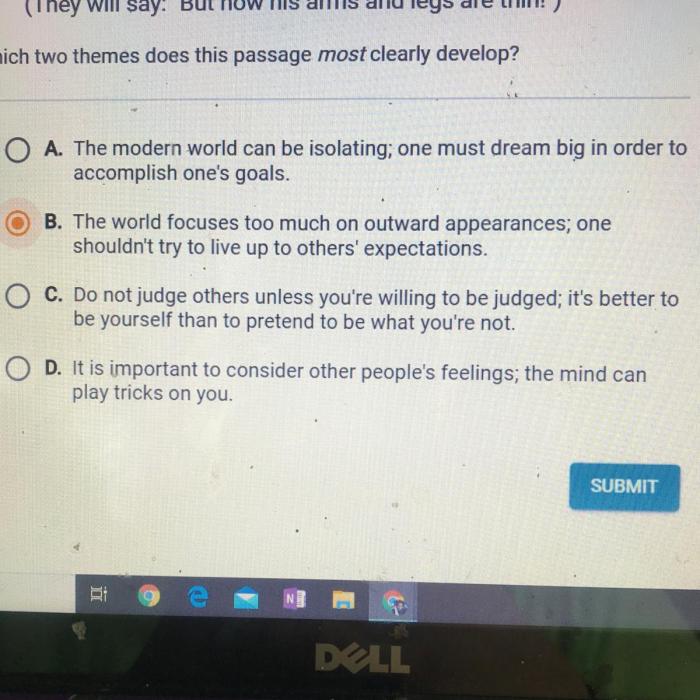
In music, consonance refers to the harmonious combination of notes that produce a pleasing or stable sound. It is the opposite of dissonance, which creates a sense of tension or instability. Consonance plays a crucial role in creating musical harmony and balance.
Consonance in Musical Intervals
Intervals are the distance between two notes. Consonant intervals are those that sound harmonious together, while dissonant intervals sound more tense. The size and ratio of intervals determine their consonance. Perfect intervals (unison, octave, perfect fourth, and perfect fifth) are considered the most consonant, while major and minor intervals (second, third, sixth, and seventh) can be either consonant or dissonant depending on their context.
Consonance in Chords
Chords are combinations of three or more notes played simultaneously. Consonant chords are those that contain predominantly consonant intervals. The arrangement and voicing of notes within a chord can affect its consonance. For example, chords with closely spaced notes tend to sound more consonant than those with widely spaced notes.
Consonance in Musical Texture
Musical texture refers to the way in which notes are arranged in a piece of music. Consonance plays a role in creating different musical textures. Homophonic textures, which feature a single melodic line accompanied by chords, often rely on consonance to create a sense of stability.
Polyphonic textures, which involve multiple independent melodic lines, can use both consonance and dissonance to create a more complex and dynamic sound.
Cultural and Historical Perspectives on Consonance, The following excerpt is consonant
The perception of consonance has varied across cultures and historical periods. In Western classical music, the major-minor system of harmony is based on the idea of consonance and dissonance. However, in other musical traditions, such as traditional Japanese music, different intervals and chords are considered consonant.
These variations reflect the cultural and aesthetic preferences of different societies.
Question Bank: The Following Excerpt Is Consonant
What is consonance in music?
Consonance refers to the harmonious and pleasing combination of musical notes, creating a sense of stability and resolution.
How does consonance affect musical intervals?
Consonant intervals, such as perfect fifths and major thirds, exhibit a harmonious relationship, producing a sense of balance and stability.
What role does consonance play in chords?
Consonant chords, composed of harmonious notes, provide a foundation for musical compositions, creating a sense of resolution and closure.