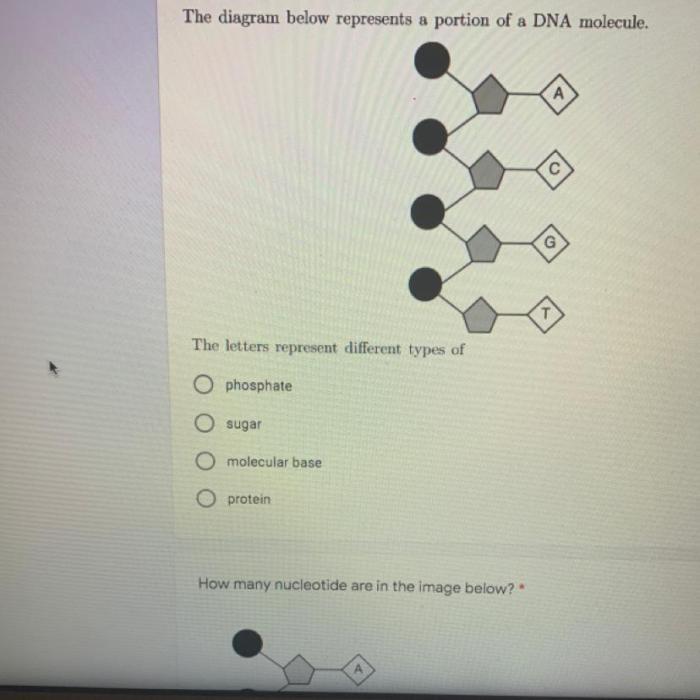
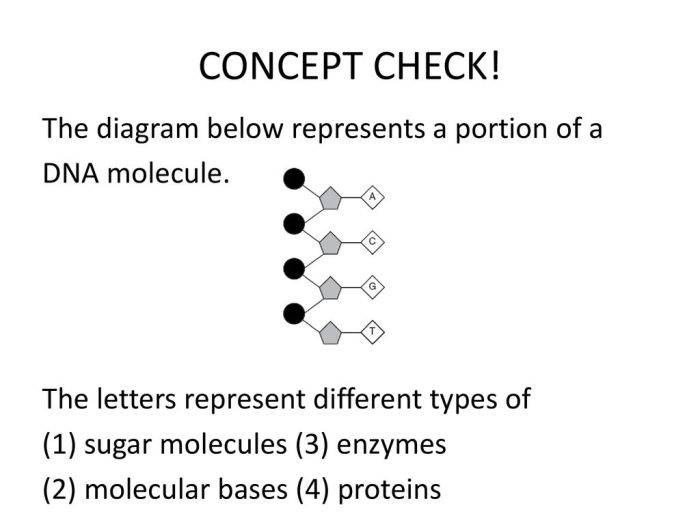
The diagram below represents a portion of a dna molecule. – The diagram below represents a portion of a DNA molecule, the fundamental building block of life. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, holds the genetic instructions that determine the characteristics of all living organisms. This molecule is made up of two strands twisted together in a double helix shape, and each strand is composed of a series of nucleotides.
Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), or guanine (G). These bases pair up in a specific way – A with T and C with G – to form the rungs of the DNA ladder.
The sequence of these bases along the DNA molecule determines the genetic code for an organism.
DNA Structure and Components: The Diagram Below Represents A Portion Of A Dna Molecule.
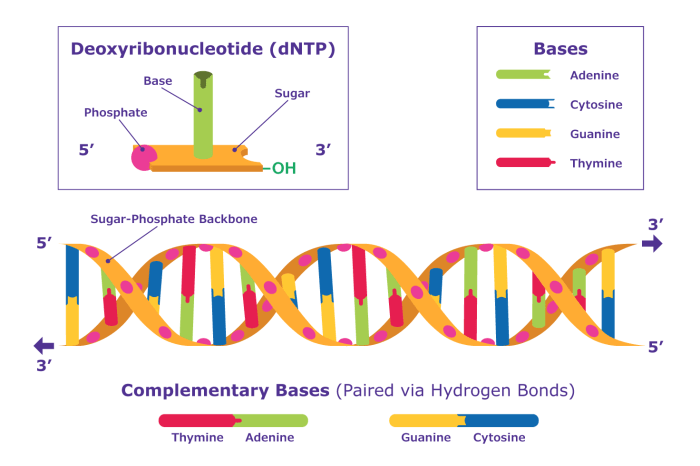
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule that contains the instructions for an organism’s development and characteristics. It is made up of two long chains of nucleotides twisted around each other to form a double helix.
Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. There are four different types of nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). The sequence of these bases along the DNA molecule determines the genetic code.
DNA Replication
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes a copy of its DNA. This process is essential for cell division, as each new cell needs its own copy of the DNA.
DNA replication is carried out by a complex of proteins, including DNA polymerase. DNA polymerase reads the sequence of bases on the original DNA molecule and adds complementary nucleotides to the new strand.
DNA Transcription
DNA transcription is the process by which the information in DNA is used to make RNA (ribonucleic acid). RNA is a molecule that is similar to DNA, but it is single-stranded and contains the base uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
DNA transcription is carried out by a complex of proteins, including RNA polymerase. RNA polymerase reads the sequence of bases on the DNA molecule and adds complementary nucleotides to the new RNA strand.
DNA Translation
DNA translation is the process by which the information in RNA is used to make proteins. Proteins are molecules that are essential for the structure and function of cells.
DNA translation is carried out by a complex of proteins, including ribosomes. Ribosomes read the sequence of bases on the RNA molecule and add amino acids to the growing protein chain.
DNA Mutations
DNA mutations are changes in the sequence of bases on the DNA molecule. Mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, including exposure to radiation, chemicals, and errors during DNA replication.
Mutations can have a variety of effects, depending on the type of mutation and the location of the mutation on the DNA molecule. Some mutations are harmless, while others can cause genetic diseases.
DNA Technologies, The diagram below represents a portion of a dna molecule.
DNA technologies are a group of techniques that are used to study and manipulate DNA. These technologies have a wide range of applications, including genetic testing, forensics, and biotechnology.
Some of the most common DNA technologies include:
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- DNA sequencing
- DNA microarrays
General Inquiries
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA is a double helix molecule composed of two strands twisted together. Each strand is made up of a series of nucleotides, which consist of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases (A, T, C, or G).
How does DNA replicate?
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes a copy of its DNA before cell division. During replication, the DNA double helix unwinds and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand.
What is DNA transcription?
DNA transcription is the process by which the information in DNA is used to create messenger RNA (mRNA). mRNA is a single-stranded molecule that carries the genetic code from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where proteins are synthesized.
What is DNA translation?
DNA translation is the process by which the information in mRNA is used to create proteins. Proteins are essential for the structure and function of cells and organisms.
What are DNA mutations?
DNA mutations are changes in the sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, including environmental toxins, radiation, and errors during DNA replication. Mutations can have a range of effects, from benign to harmful.