Correctly label the following parts of a chemical synapse – Embark on a scientific exploration of chemical synapses, the intricate junctions that facilitate communication between neurons. This comprehensive guide will delve into their structure, function, and significance in neural circuits, providing a foundation for understanding the fundamental mechanisms of brain function.
Chemical synapses are specialized structures that enable neurons to transmit signals across a synaptic cleft. They consist of a presynaptic terminal, postsynaptic membrane, and synaptic cleft, each with distinct roles in neurotransmission.
Components of a Chemical Synapse
Chemical synapses are specialized junctions that allow neurons to communicate with each other. They consist of three main components: the presynaptic terminal, the postsynaptic membrane, and the synaptic cleft.
Presynaptic Terminal
The presynaptic terminal is the part of the neuron that releases neurotransmitters. It contains vesicles filled with neurotransmitters, as well as proteins that help to release them. When an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft.
Postsynaptic Membrane
The postsynaptic membrane is the part of the neuron that receives neurotransmitters. It contains receptors that bind to neurotransmitters and trigger a response in the neuron. The response can be excitatory, causing the neuron to fire an action potential, or inhibitory, preventing the neuron from firing an action potential.
Synaptic Cleft, Correctly label the following parts of a chemical synapse
The synaptic cleft is the space between the presynaptic terminal and the postsynaptic membrane. It is filled with extracellular fluid that allows neurotransmitters to diffuse from the presynaptic terminal to the postsynaptic membrane.
Neurotransmitter Release and Binding: Correctly Label The Following Parts Of A Chemical Synapse
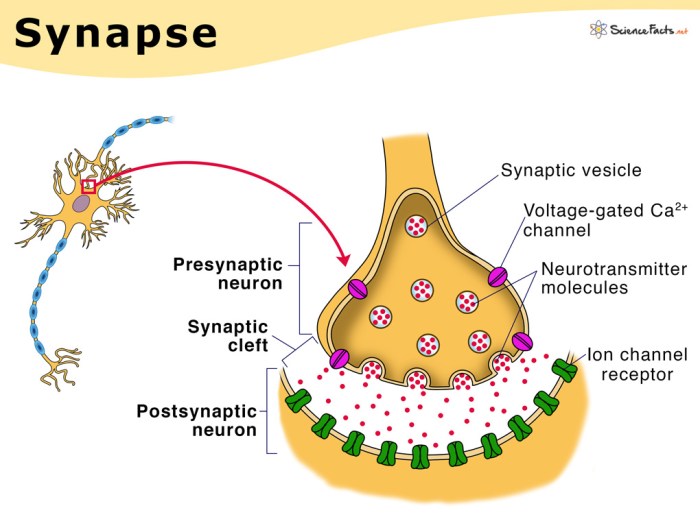
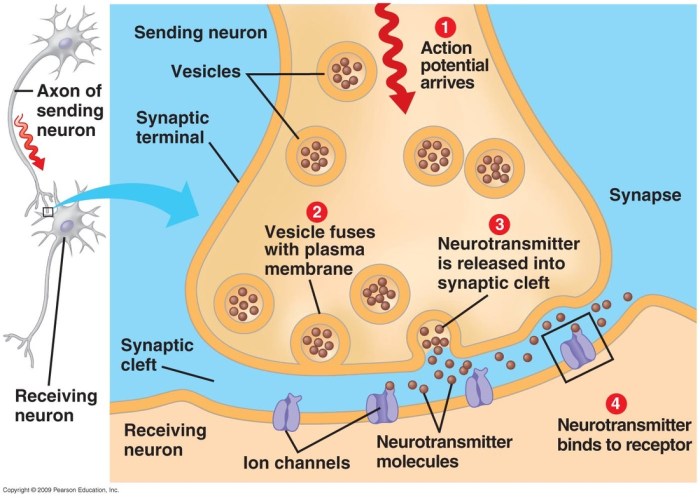
Neurotransmitters are synthesized in the presynaptic terminal and stored in vesicles. When an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitters then diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.The
binding of neurotransmitters to receptors triggers a response in the neuron. The response can be excitatory, causing the neuron to fire an action potential, or inhibitory, preventing the neuron from firing an action potential.
Synaptic Plasticity
Synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to change their strength over time. This is a fundamental property of the brain that allows it to learn and adapt. There are two main types of synaptic plasticity: long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD).LTP
is a strengthening of a synapse that occurs when the presynaptic neuron fires repeatedly at high frequency. LTD is a weakening of a synapse that occurs when the presynaptic neuron fires repeatedly at low frequency.Synaptic plasticity is thought to be the cellular basis of learning and memory.
Role of Chemical Synapses in Neural Communication
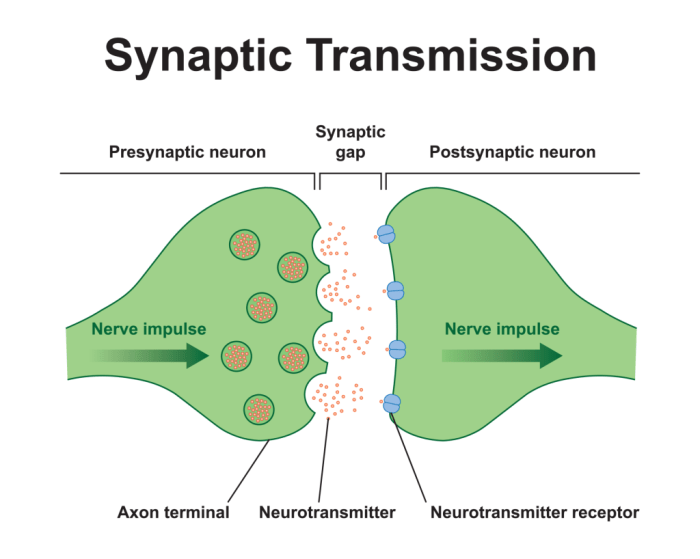
Chemical synapses are essential for neural communication. They allow neurons to transmit signals to each other, forming neural circuits that underlie brain function. Disruptions in chemical synaptic function can lead to a variety of neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
Essential FAQs
What is the role of the presynaptic terminal?
The presynaptic terminal is responsible for synthesizing, storing, and releasing neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft.
How do neurotransmitters bind to postsynaptic receptors?
Neurotransmitters bind to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, triggering a cascade of events that can either excite or inhibit the postsynaptic neuron.
What is synaptic plasticity?
Synaptic plasticity refers to the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, which is a fundamental mechanism for learning and memory.