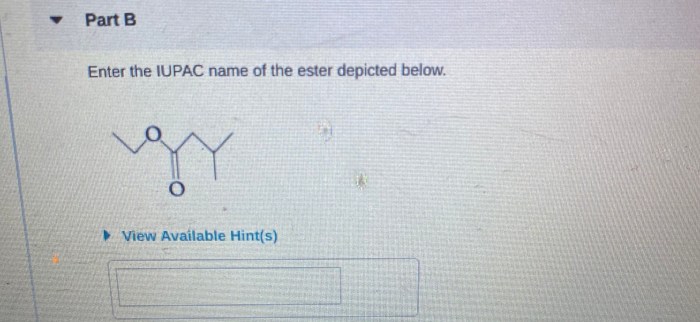
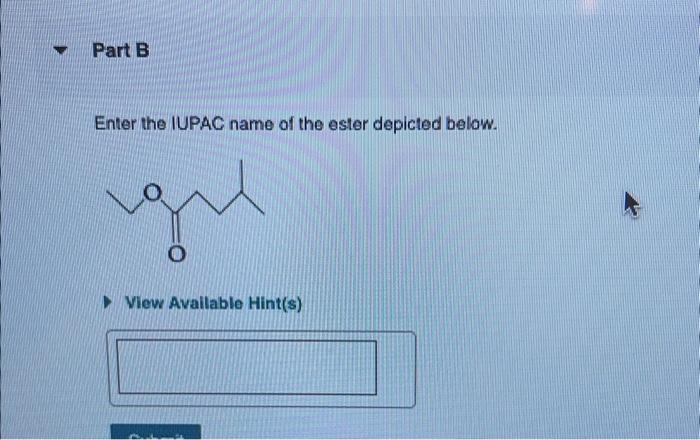
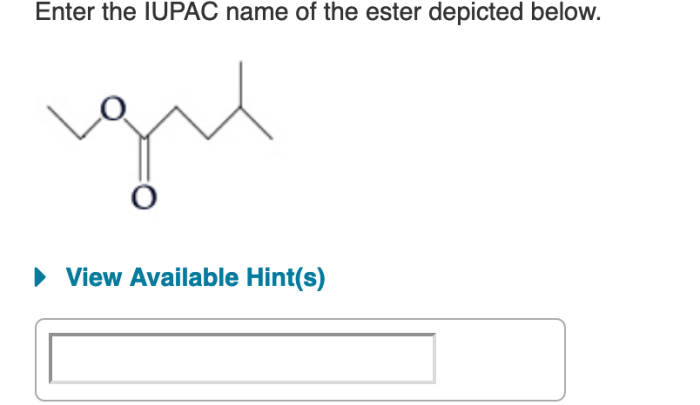
Enter the IUPAC name of the ester depicted below. This task delves into the realm of organic chemistry, where we unravel the intricacies of naming organic compounds according to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) guidelines. Embark on this journey to master the art of systematic nomenclature and unlock the secrets hidden within the molecular structure of esters.
As we delve deeper into the topic, we will explore the fundamental principles governing IUPAC nomenclature for esters. We will meticulously dissect the structural components of an ester, identifying functional groups, parent chains, and substituents. Armed with this knowledge, we will embark on a step-by-step guide to constructing IUPAC names, ensuring accuracy and precision in our chemical communication.
IUPAC Nomenclature for Esters: Enter The Iupac Name Of The Ester Depicted Below.
Esters are organic compounds characterized by the presence of an ester functional group, which consists of a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to an alkoxy group (OR). The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) system provides a set of rules for naming esters systematically.
Principles of IUPAC Nomenclature for Esters, Enter the iupac name of the ester depicted below.
The IUPAC nomenclature for esters involves identifying the parent chain, which is the longest carbon chain containing both the carbonyl and alkoxy groups. The name of the ester is derived from the names of the alkyl groups attached to the carbonyl and alkoxy groups.
Structural Analysis of the Given Ester
The given ester has the following structural formula:“`CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH3“`The functional groups present are:
- Carbonyl group (C=O)
- Alkoxy group (OCH2CH3)
The parent chain is butane (four carbon atoms), which contains both the carbonyl and alkoxy groups. The alkyl group attached to the carbonyl carbon is ethyl (two carbon atoms), and the alkyl group attached to the alkoxy group is methyl (one carbon atom).
Naming the Ester
To name the ester, we combine the names of the alkyl groups attached to the carbonyl and alkoxy groups. The name of the alkyl group attached to the carbonyl carbon is placed first, followed by the name of the alkyl group attached to the alkoxy group.
The suffix “-oate” is added to the end of the name to indicate the presence of the ester functional group.In this case, the alkyl group attached to the carbonyl carbon is ethyl, and the alkyl group attached to the alkoxy group is methyl.
Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given ester is:Ethyl methanoate
Example
Consider the following ester:“`CH3CH2CH2COOCH(CH3)2“`The parent chain is pentane (five carbon atoms), which contains both the carbonyl and alkoxy groups. The alkyl group attached to the carbonyl carbon is propyl (three carbon atoms), and the alkyl group attached to the alkoxy group is isopropyl (three carbon atoms).The
IUPAC name of this ester is:Propyl isopropanoate
FAQ Insights
What is the purpose of IUPAC nomenclature?
IUPAC nomenclature provides a systematic and universally accepted method for naming chemical compounds, ensuring consistency and clarity in scientific communication.
How do I determine the parent chain of an ester?
The parent chain is the longest continuous carbon chain that contains both the ester functional group and the alkyl group attached to the oxygen atom.
What is the difference between a prefix and a suffix in IUPAC nomenclature?
Prefixes indicate the number of carbon atoms in a substituent group, while suffixes indicate the type of functional group present.