Resin based composite three surfaces posterior – Resin-based composite three surfaces posterior restorations have revolutionized dentistry, offering a versatile and durable solution for posterior tooth restoration. This article provides a comprehensive overview of resin-based composite three surfaces posterior, encompassing their composition, clinical applications, bonding techniques, finishing and polishing techniques, evaluation criteria, and factors affecting longevity.
The unique properties of resin-based composites, including their excellent aesthetics, low polymerization shrinkage, and bond strength to dentin and enamel, make them an ideal choice for restoring posterior teeth. This article delves into the clinical indications and step-by-step procedures for placing resin-based composite three surfaces posterior restorations, ensuring optimal outcomes and patient satisfaction.
1. Introduction to Resin-Based Composite Three Surfaces Posterior
Resin-based composite materials are a type of dental restorative material that is used to repair and restore damaged teeth. They are composed of a resin matrix, which is a type of plastic, and a filler material, which is usually glass or ceramic.
Resin-based composites are strong, durable, and have a natural appearance, which makes them a good choice for restoring posterior teeth.Resin-based composites offer several advantages over other types of restorative materials, such as amalgam and gold. They are more conservative, meaning that they require less tooth structure to be removed in order to place the restoration.
They are also more esthetic, as they can be matched to the color of the surrounding teeth. Additionally, resin-based composites are less likely to cause sensitivity or allergic reactions.However, resin-based composites also have some disadvantages. They are more expensive than other types of restorative materials, and they can be more difficult to place.
Additionally, resin-based composites are more susceptible to wear and tear than other types of restorative materials.
2. Clinical Applications of Resin-Based Composite Three Surfaces Posterior
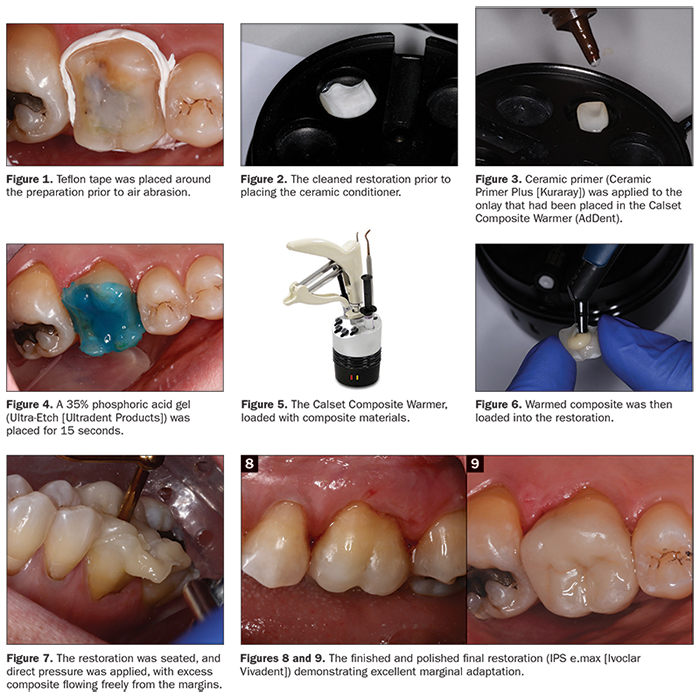
Resin-based composites are indicated for use in a variety of clinical situations, including:
- Restoring posterior teeth with three or more missing surfaces
- Replacing old or failing amalgam or gold restorations
- Repairing fractured teeth
- Improving the esthetics of discolored or misshapen teeth
The step-by-step procedure for placing a resin-based composite three surfaces posterior restoration is as follows:
- Prepare the tooth by removing any decay or old restoration.
- Etch the tooth with a phosphoric acid gel to create a rough surface that will allow the bonding agent to adhere to the tooth.
- Apply a bonding agent to the tooth and light-cure it.
- Place the resin-based composite material into the prepared cavity and light-cure it.
- Contour and polish the restoration.
3. Bonding Techniques for Resin-Based Composite Three Surfaces Posterior
There are two main bonding techniques that can be used for resin-based composite three surfaces posterior restorations:
-
-*Self-etching bonding
This technique uses a bonding agent that contains an acid that etches the tooth and primes it for bonding in one step.
-*Etch-and-rinse bonding
This technique uses a separate etching gel and bonding agent. The etching gel is applied to the tooth first, and then the bonding agent is applied.
The choice of bonding technique depends on the clinical situation. Self-etching bonding is easier to use and less time-consuming, but it may not be as strong as etch-and-rinse bonding. Etch-and-rinse bonding is stronger, but it is more technique-sensitive and can be more time-consuming.
4. Finishing and Polishing Techniques for Resin-Based Composite Three Surfaces Posterior: Resin Based Composite Three Surfaces Posterior
Proper finishing and polishing are essential for the longevity of a resin-based composite restoration. Finishing involves removing any excess material from the restoration and smoothing the surface. Polishing involves creating a smooth, glossy surface that will resist wear and tear.There
are a variety of finishing and polishing tools that can be used for resin-based composite restorations, including:
-
-*Rotary instruments
Rotary instruments, such as burs and diamonds, can be used to remove excess material and contour the restoration.
-*Hand instruments
Hand instruments, such as files and scalers, can be used to refine the shape of the restoration and remove any sharp edges.
-*Polishing pastes and wheels
Polishing pastes and wheels can be used to create a smooth, glossy surface on the restoration.
The finishing and polishing procedure should be tailored to the specific restoration. In general, it is important to start with a coarse-grit instrument and gradually move to a finer-grit instrument. It is also important to use a light touch and avoid overheating the restoration.
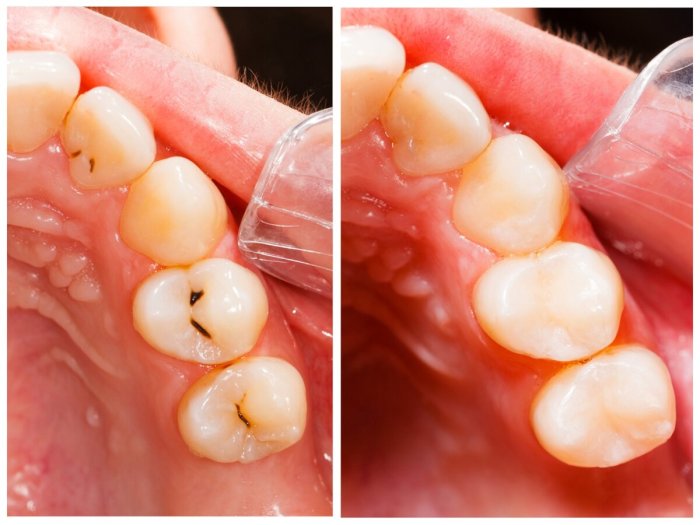
5. Evaluation of Resin-Based Composite Three Surfaces Posterior

The clinical evaluation of resin-based composite three surfaces posterior restorations should include an assessment of the following criteria:
-
-*Marginal adaptation
The restoration should have good marginal adaptation, meaning that it should fit tightly against the tooth without any gaps or overhangs.
-*Occlusal contacts
The restoration should have proper occlusal contacts, meaning that it should meet the opposing teeth evenly and without any premature contacts.
-*Color match
The restoration should be matched to the color of the surrounding teeth.
-*Surface texture
The restoration should have a smooth, glossy surface.
-*Longevity
The restoration should last for many years without any major problems.
The factors that can affect the longevity of resin-based composite three surfaces posterior restorations include:
-
-*The skill of the dentist
The dentist’s skill in placing and finishing the restoration can have a significant impact on its longevity.
-*The patient’s oral hygiene
The patient’s oral hygiene habits can also affect the longevity of the restoration. Patients who do not brush and floss regularly are more likely to develop decay around the restoration.
-*The type of restoration
The type of restoration can also affect its longevity. Restorations that are placed in areas of high stress, such as the back teeth, are more likely to fail than restorations that are placed in areas of low stress, such as the front teeth.
FAQ Corner
What are the advantages of using resin-based composites for posterior restorations?
Resin-based composites offer several advantages for posterior restorations, including excellent aesthetics, low polymerization shrinkage, bond strength to dentin and enamel, and versatility in shaping and contouring.
What are the different bonding techniques used for resin-based composite three surfaces posterior restorations?
The most common bonding techniques for resin-based composite three surfaces posterior restorations include self-etch adhesives, etch-and-rinse adhesives, and universal adhesives.
What is the importance of proper finishing and polishing for resin-based composite three surfaces posterior restorations?
Proper finishing and polishing are crucial for the longevity of resin-based composite three surfaces posterior restorations. They remove excess material, refine the anatomy, and create a smooth surface that is less susceptible to wear and tear.