The Blood Types and Transfusions Worksheet serves as an invaluable resource for comprehending the complexities of blood types and transfusions. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of blood group systems, compatibility, and transfusion principles, providing a thorough understanding of this critical medical topic.
Delving into the fundamentals of blood types, the worksheet elucidates the ABO blood group system and its associated antigens. The significance of the Rh factor is meticulously examined, shedding light on its impact on blood compatibility. Furthermore, the guide presents practical examples of blood type combinations and their compatibility, offering a clear understanding of transfusion possibilities.
Blood Types and Compatibility
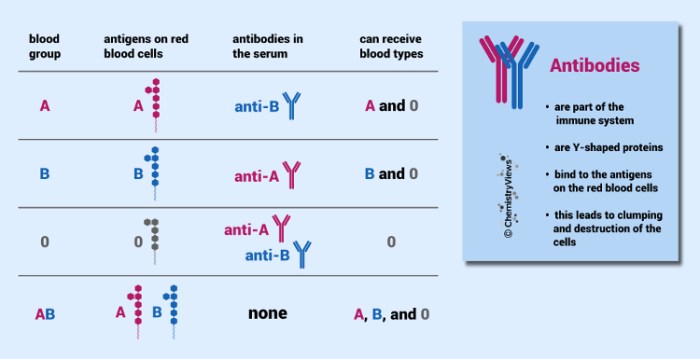
Blood types are determined by the presence or absence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells. The ABO blood group system is the most important blood group system, and it consists of four blood types: A, B, AB, and O.
The Rh factor is another important blood group antigen. Rh-positive individuals have the Rh antigen on their red blood cells, while Rh-negative individuals do not. The Rh factor is not as important as the ABO blood group system in determining blood compatibility, but it can still cause problems in some cases.
Blood Type Combinations and Compatibility
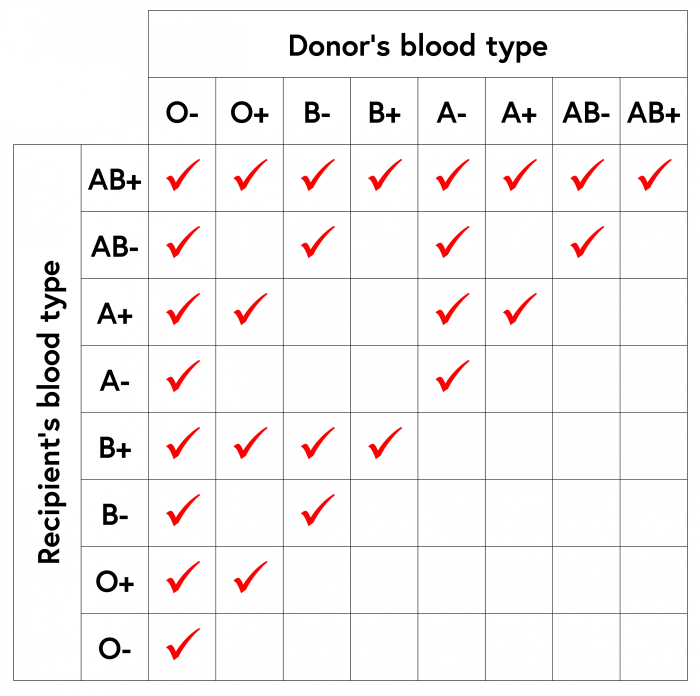
When a blood transfusion is given, the donor’s blood must be compatible with the recipient’s blood. If the blood is not compatible, the recipient’s immune system will attack the donor’s red blood cells, causing a transfusion reaction.
- Type A blood can receive transfusions of type A or O blood.
- Type B blood can receive transfusions of type B or O blood.
- Type AB blood can receive transfusions of any blood type.
- Type O blood can only receive transfusions of type O blood.
Blood Transfusion Principles
Indications for Blood Transfusions, Blood types and transfusions worksheet
- To treat anemia
- To replace blood lost due to surgery or trauma
- To prevent bleeding in patients with certain medical conditions
Contraindications for Blood Transfusions
- If the recipient has a history of transfusion reactions
- If the recipient has a rare blood type
- If the recipient is pregnant
Cross-Matching
Cross-matching is a laboratory test that is used to determine if the donor’s blood is compatible with the recipient’s blood. The test is performed by mixing a sample of the donor’s blood with a sample of the recipient’s serum. If the serum causes the donor’s red blood cells to agglutinate (clump together), the blood is not compatible and the transfusion cannot be given.
Risks and Complications of Blood Transfusions
- Transfusion reactions
- Hemolytic transfusion reactions
- Anaphylactic reactions
- Infections
Blood Transfusion Practice: Blood Types And Transfusions Worksheet
Step-by-Step Guide to Administering a Blood Transfusion
- Verify the patient’s identity and blood type.
- Cross-match the donor’s blood with the recipient’s blood.
- Start the blood transfusion.
- Monitor the patient for any signs of a transfusion reaction.
Monitoring and Management of Patients Receiving Blood Transfusions
Patients receiving blood transfusions should be monitored for any signs of a transfusion reaction. These signs include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Hives
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
If any of these signs occur, the transfusion should be stopped and the doctor should be notified immediately.
Blood Types, Antigens, and Compatible Transfusions
| Blood Type | Antigens | Compatible Transfusions |
|---|---|---|
| A | A | A, O |
| B | B | B, O |
| AB | A, B | A, B, AB, O |
| O | None | O |
Quick FAQs
What are the different blood types?
The main blood groups are A, B, AB, and O, determined by the presence or absence of specific antigens on red blood cells.
What is the Rh factor?
The Rh factor is another antigen found on red blood cells. People who have the Rh antigen are Rh-positive, while those who do not are Rh-negative.
Why is blood compatibility important in transfusions?
Transfusing incompatible blood can lead to a life-threatening reaction called hemolytic transfusion reaction, where the recipient’s immune system attacks the transfused red blood cells.